
IdentificationPhysical DataSpectraRoute of Synthesis (ROS)Safety and HazardsOther Data
Identification
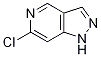
Product Name6-Chloro-1H-pyrazolopyridineIUPAC Name6-chloro-1H-pyrazolopyridine Molecular StructureCAS Registry Number 1206979-33-0MDL NumberMFCD17010105Synonyms6-Chloro-1H-pyrazolopyridine1206979-33-0DTXSID407188946-Chloro-1H-pyrazolo(4,3-c)pyridineDTXCID90669640808-339-3MFCD17010105SCHEMBL5066090AAJIQIWPVIWCGA-UHFFFAOYSA-NBCP05299BBL100380STL554174AKOS015919537CS-W019595PB25597SY020932TS-02049DB-050724EN300-97955Molecular FormulaC6H4ClN3Molecular Weight153.57InChIInChI=1S/C6H4ClN3/c7-6-1-5-4(2-8-6)3-9-10-5/h1-3H,(H,9,10)InChI KeyAAJIQIWPVIWCGA-UHFFFAOYSA-NSMILESCC1=C2C(=CN=C1Cl)C=NN2
Patent InformationPatent IDTitlePublication DateUS2014/171405Fused Pyrazoles as FGFR Inhibitors2014WO2013/17479PYRAZOLOPYRIDINE DERIVATIVES AS JAK INHIBITORS2013WO2013/17480PYRAZOLOPYRIDINE DERIVATIVES AS JAK INHIBITORS2013
Physical Data
AppearanceLight yellow to brown solidSolubilitySoluble in ethanol
Spectra
Description (NMR Spectroscopy)Nucleus (NMR Spectroscopy)Solvents (NMR Spectroscopy)Frequency (NMR Spectroscopy), MHzChemical shifts1Hdimethylsulfoxide-d6400
6-Chloro-1H-pyrazolopyridine CAS#: 1206979-33-0 NMR
Route of Synthesis (ROS)
Route of Synthesis (ROS) of 6-Chloro-1H-pyrazolopyridine CAS 1206979-33-0
ConditionsYieldWith 4-methylbenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride In 1,4-dioxane at 110℃;Experimental Procedure76.A 6-chloro-1-(tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)-1H-pyrazolopyridineA mixture of 6-chloro-1H-pyrazolopyridine (11.5 g, 0.075 mol) and 3,4-dihydro-2H-pyran (19 g, 0.225 mol) and Tos-OH (0.13 g 0. 75 mmol) in 1,4-dioxane (175 mL) was heated at 110 °C overnight. The mixture was cooled to room temperature and concentrated. The crude product was purified by column chromatography on silica gel (petroleum ether ethylacetate 20:0~20: 1) to afford a mixture of 6-chloro-1-(tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)-1H-pyrazolopyridine and 6-chloro-2-(tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)-2H-pyrazolopyridine (13.5 g, yield 76 %) MS (ESI) m/z: m/z: 238 +.76%With toluene-4-sulfonic acid In 1,4-dioxane at 110℃; for 18h;76%With toluene-4-sulfonic acid In dichloromethane for 24h; Reflux;Experimental Procedure149 Preparation 1496-Chloro-1 -(tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)- 1 H-pyrazolopyridinePreparation 1496-Chloro-1 -(tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)- 1 H-pyrazolopyridine10684] To a solution of 6-chloro-1H-pyrazolopyri- dine (75 g, 488.37 mmol) in DCM (2 L) was added dihydropyran (66.98 mE, 732.56 mmol) followed by para-toluenesulfonic acid (18.58 g, 97.67 mmol) and the reaction was heated to reflux for 18 hours. Further para-toluenesulfonic acid (0.1 eq) and dihydropyran (0.75 eq) were added and the reaction continued heating at reflux for 6 hours. The reaction was cooled and quenched with saturated aqueous sodium bicarbonate solution. The organic layer was collected, washed with brine, dried over sodium sulfate and concentrated in vacuo. The residue was purified using silica gel column chromatography eluting with 17% EtOAc in hexanes followed by trituration with ether to afford the title compound as a pale yellow solid (83 g, 72%). ‘H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d5): öppm 1.59 (m, 2H), 1.71 (m, 1H), 2.02 (m, 2H), 2.29 (m, 1H), 3.74 (m, 1H), 3.89 (m, 1H), 5.91 (m, 1H), 7.93 (s, 1H), 8.38 (s, 1H), 8.94 (s, 1H).72%With toluene-4-sulfonic acid In dichloromethane at 45℃; for 16h;Experimental Procedure1 Step 1: 6-(hloro-l -(tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)-1H-pyrazolo|4,-c|pyridine A mixture of 6-chloro-1H-pyrazolopyridine(3 g, 19.54 mmol),DHP (5.4 mL, 58.61 mmol), and TsOH H2O (743 mg, 3.91 mmol) in DCM (40 mL) was stirred at 45 °C for 16 h, allowed to cool to rt, adjusted to pH=7 with sat. aq. NaHCO3, and then extracted with DCM (3 x30 mL). The combined organic layers were washed with brine (30 mL), dried (Na2SO4), filtered, concentrated, and then purified by silica gel chromatography (petroleum ether/ethyl acetate=30: 1 to 3 : 1) to give 6-chloro- 1 -(tetrahydro-2H -pyran-2-yl)- l H-pyrazolopyridine (2.8 g, 60%) as a yellow solid. 1HNMR(400 MHz, DDDMSO-d δ6): 8.95 (d, 1H), 8.38 (s, 1H), 7.93 (s, 1H), 5.91 (dd, 1H), 3.90-3.87 (m, 1H), 3.79-3.73 (m, 1H), 2.36-2.32 (m, 1H), 2.03-1.95 (m, 2H), 1.73-1.69 (m, 1H), 1.60-1.55 (m, 2H); LCMS: 238.1 +.60%With methanesulfonic acid In tetrahydrofuran; dichloromethane at 20 - 50℃;Experimental Procedure24.1 6-chloro-1-(tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)-1H-pyrazolopyridineAt r.t. to a suspension of 6-chloro-1H-pyrazolopyridine (0.5 g, 3 mmol) (Frontier Cat. No. Z13659) in methylene chloride (3 mL) and THF (1 mL) was added methanesulfonic acid (42 μL, 0.65 mmol), followed by dihydropyran (0.89 mL, 9.8 mmol).The mixture was stirred at r.t. for 2 h., and then at 50° C. overnight.After cooling the mixture was concentrated under reduced pressure.The residue was purified by flash chromatography on a silica gel column with ethyl acetate in hexanes (0-50%) to afford the desired product (0.8 g). LCMS (M+H)+=238.0; LCMS (M-84+H)+=154.0/156.0.0.8 g
Safety and Hazards
Pictogram(s)SignalWarningGHS Hazard StatementsH302 (100%): Harmful if swallowed Precautionary Statement CodesP264, P270, P301+P317, P330, and P501(The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.)
Other Data
TransportationUnder room temperature away from lightStorageUnder room temperature away from lightShelf Life2 years
DruglikenessLipinski rules componentMolecular Weight153.571logP1.607HBA3HBD1Matching Lipinski Rules4Veber rules componentPolar Surface Area (PSA)41.57Rotatable Bond (RotB)0Matching Veber Rules2
Use PatternThe compound, featuring a pyrazolopyridine structure, is primarily used as a pharmaceutical intermediate. It plays a crucial role in the synthesis of targeted kinase inhibitors, such as PI3K, JAK, and BTK inhibitors, as well as drugs for central nervous system disorders. It often serves as a core scaffold in the development of anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, antiviral, and neurological therapeutics. In drug discovery, this structure is highly valued for its biological activity and versatility. The presence of a chlorine atom allows for further functionalization through reactions such as Suzuki or Buchwald couplings, enabling the construction of more complex molecules. Additionally, this compound is frequently employed in early-stage drug research, particularly in high-throughput screening (HTS) and structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies, making it a valuable tool in the identification and optimization of lead compounds. https://www.chemwhat.com/6-chloro-1h-pyrazolo43-cpyridine-cas-1206979-33-0/
Comments
Post a Comment